In recent years, 3D laser scanning companies have quietly revolutionized the way industries operate, design, and innovate. From construction sites and historical preservation efforts to manufacturing plants and forensic investigations, the applications of this powerful technology are expanding rapidly. Although the term “3D laser scanning” might once have sounded futuristic, it has firmly established itself as an indispensable tool across a wide range of sectors. Understanding how it works and why it is so transformative offers a glimpse into the future of precision and efficiency.
- What is 3D Laser Scanning?
- Why 3D Laser Scanning is Gaining Popularity
- Applications Across Industries
- Construction and Architecture
- Manufacturing and Industrial Facilities
- Historical Preservation
- Law Enforcement and Forensics
- How 3D Laser Scanning Works
- The Role of 3D Laser Scanning Companies
- Choosing the Right 3D Laser Scanning Company
- The Future of 3D Laser Scanning
- Conclusion
What is 3D Laser Scanning?
At its core, 3D laser scanning is a technology that captures the exact shape and size of physical objects by using laser light. A scanner emits a laser beam that measures millions of points across a surface, generating a “point cloud” — a detailed digital representation of the scanned area or object. This point cloud can then be processed into 3D models, blueprints, or digital twins, which are used for analysis, replication, and design improvements.
The beauty of 3D laser scanning lies in its unparalleled precision. It captures complex geometries with remarkable speed, eliminating many of the inefficiencies associated with traditional manual measurement methods.
Why 3D Laser Scanning is Gaining Popularity
One of the main reasons 3D laser scanning companies are increasingly in demand is their ability to offer accurate, high-resolution data in a fraction of the time it would take using conventional surveying methods. In industries where a small miscalculation can lead to costly errors or safety hazards, having access to precise measurements can make all the difference.
Moreover, the non-contact nature of laser scanning makes it ideal for delicate or hazardous environments. Technicians can gather data from a safe distance without disturbing fragile artifacts, unstable structures, or dangerous work zones.
Another key advantage is the creation of digital archives. Whether preserving historic buildings, creating as-built documentation for renovation projects, or capturing factory layouts, 3D scans provide a detailed and permanent digital record that can be referenced long after the physical subject has changed or disappeared.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of 3D laser scanning companies has allowed them to serve a broad spectrum of industries, each harnessing the technology to meet their unique needs.
Construction and Architecture
In construction, accurate measurements are critical to ensuring projects stay on schedule and within budget. 3D laser scanning is used for site surveys, clash detection, and quality assurance, allowing teams to identify and resolve issues before they become costly problems. Architects rely on the technology to create precise models of existing structures, streamlining renovation and retrofit projects.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has also greatly benefited from 3D scanning. Scans can be integrated into BIM software, providing a seamless transition from the real world to the digital design phase. This integration promotes better collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors.
Manufacturing and Industrial Facilities
Manufacturers turn to 3D laser scanning to optimize factory layouts, reverse-engineer parts, and ensure quality control. Scanning an object allows engineers to analyze deviations from design specifications down to fractions of a millimeter, helping maintain rigorous production standards.
In industrial facilities, the technology assists in maintenance planning and equipment installation. By providing detailed spatial data, companies can avoid costly shutdowns and enhance worker safety by minimizing risks associated with tight spaces and complex machinery arrangements.
Historical Preservation
Preserving the past has always been a challenging endeavor, particularly when dealing with fragile, aging structures. 3D laser scanning companies are instrumental in the documentation and restoration of historical sites, monuments, and artifacts. High-resolution scans allow preservationists to create detailed digital replicas that can be studied, shared, and even reconstructed if necessary.
In many cases, 3D scanning provides insights that would be difficult or impossible to obtain through traditional methods. For example, subtle structural shifts or material degradation can be detected long before they are visible to the naked eye.
Law Enforcement and Forensics
Crime scene investigators increasingly employ 3D laser scanning to capture scenes with unparalleled accuracy. Detailed, time-stamped scans preserve evidence exactly as it was found, allowing forensic experts to analyze scenes long after they have been cleared. This can be invaluable for reconstructing accidents, understanding ballistic trajectories, and presenting clear, visual evidence in courtrooms.
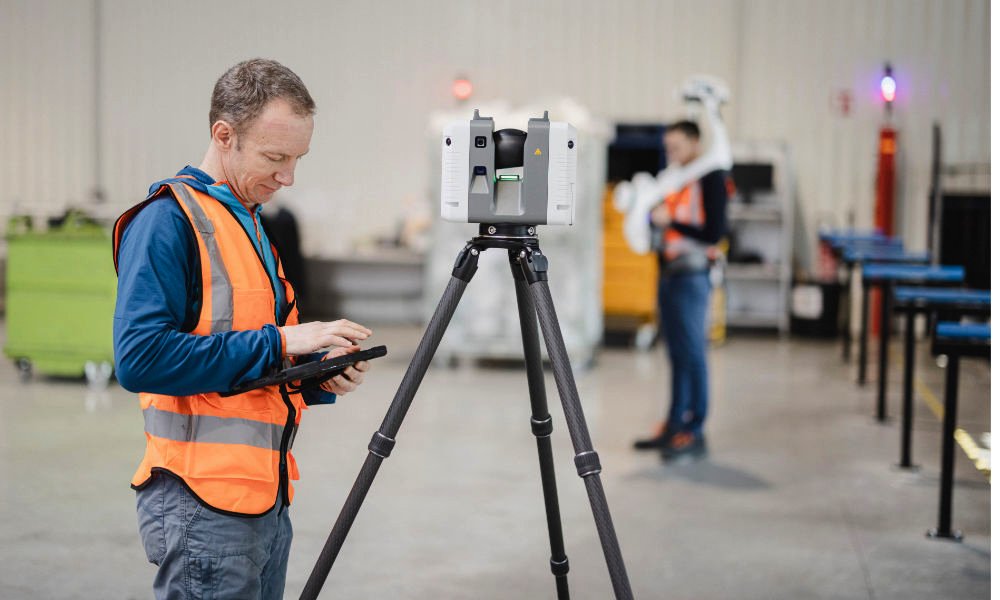
How 3D Laser Scanning Works
While the technical intricacies behind 3D laser scanning are complex, the basic process typically involves three main steps: scanning, processing, and modeling.
During the scanning phase, a laser scanner is positioned to capture the target area or object. Depending on the project, multiple scans from different angles may be required to create a complete dataset. The scanner measures millions of points by detecting the time it takes for the laser beam to bounce back from surfaces — a method known as time-of-flight measurement.
The next step involves processing the data. Specialized software organizes the raw point cloud into a coherent structure, aligning and cleaning up the data to eliminate noise or irrelevant points.
Finally, the processed data is transformed into usable 3D models or drawings. These models can be integrated into CAD software, BIM programs, or custom visualization tools, depending on the intended use.
The Role of 3D Laser Scanning Companies
3D laser scanning companies play a pivotal role in making this technology accessible and practical for a variety of clients. Their expertise extends beyond operating scanners; it includes project planning, data interpretation, modeling, and integration into broader workflows.
Not all projects are created equal. Some may require handheld scanners for tight indoor spaces, while others need long-range scanners capable of mapping expansive outdoor environments. Choosing the right equipment and methodology is crucial for success, and experienced scanning companies know how to tailor solutions to specific project demands.
Additionally, these companies often provide consulting services, helping clients understand the best ways to leverage scanned data for project efficiency, compliance, and innovation.
Choosing the Right 3D Laser Scanning Company
When selecting among 3D laser scanning companies, several factors come into play. Experience and technical expertise are, of course, essential. It’s also important to consider a company’s portfolio — what industries they have worked in, the scale of projects they’ve completed, and the technologies they specialize in.
Data security and confidentiality are other important considerations, particularly in sensitive industries like defense, healthcare, or critical infrastructure. Clients must ensure that their chosen company adheres to strict data protection standards.
Finally, customer service and communication matter. A good scanning company should act as a collaborative partner, guiding clients through the scanning process, addressing questions, and offering actionable insights based on collected data.
The Future of 3D Laser Scanning
The future for 3D laser scanning companies looks bright as technological advancements continue to refine and expand their capabilities. Innovations in drone-mounted scanners, mobile scanning devices, and real-time data processing are making it easier than ever to capture and analyze environments on the go.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also beginning to play a role, helping automate the interpretation of scanned data. This could soon enable faster identification of patterns, defects, or anomalies without extensive human input.
Moreover, as industries like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) grow, the detailed digital twins created through 3D scanning will find new applications. Virtual walk-throughs of buildings, remote site inspections, and interactive design reviews are just a few examples of the possibilities ahead.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning companies are not merely service providers; they are enablers of progress across diverse sectors. By offering precision, efficiency, and digital foresight, they help businesses, governments, and researchers work smarter and achieve results that were once unimaginable.
As this technology becomes even more accessible and powerful, its role in shaping the future of industries and communities will only deepen. Those who embrace it early are positioning themselves at the forefront of innovation, ready to unlock new levels of accuracy, creativity, and success.